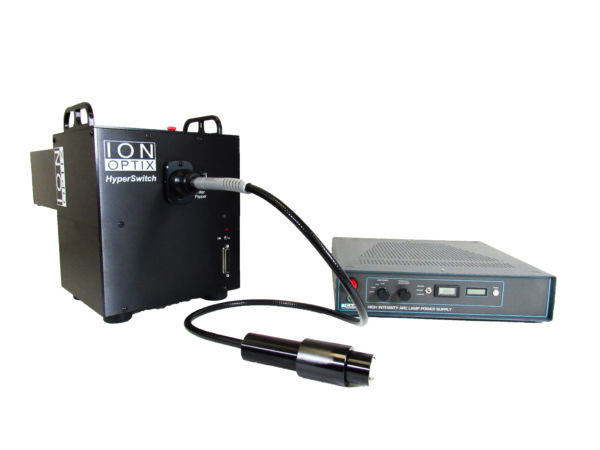
HyperSwitch Light Source
In cases where highest time resolution is essential, the IonOptix HyperSwitch Light Source is recommended. Wavelength switching is accomplished in less than 1msec and can be continuously alternated at rates as high as 250 pairs/sec. The HyperSwitch can also produce hardware video-locked wavelength switching.
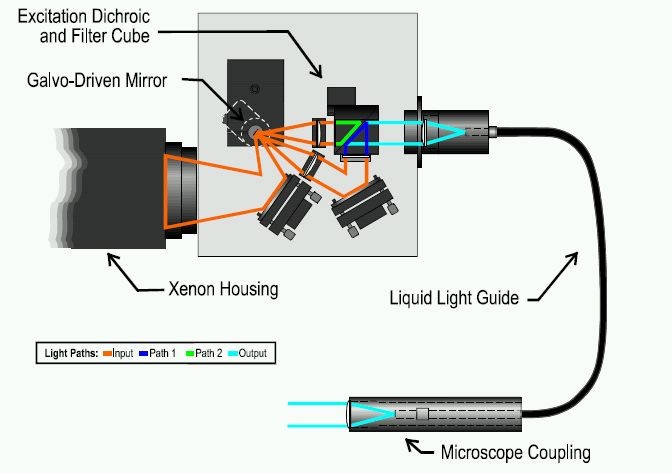
This figure illustrates the optical path and components of the IonOptix HyperSwitch Dual Excitation Light Source. The light output of a 75 W xenon-arc bulb is formed into a converging beam using a parabolic reflector within the xenon housing. A front-surface beam steering mirror positions the focal point of the beam just beyond a galvo-driven mirror that rapidly alternates between two separate paths. In path 1, the now diverging xenon light is collimated by a quartz lens and is then steered into the “side” input of the excitation dichroic cube (EDC). In path 2, a second lens collimates the xenon light before it enters the “front” input of the EDC. In addition, the mirror may also be set to a third position that provides high speed shuttering of the excitation light by directing the light away from both input paths. Separate filters on each input of the EDC filter the xenon light to create the individual excitation wavelengths. A dichroic mirror inside the EDC passes the filtered path 2 light to the “rear” output of the EDC as well as reflects the filtered path 1 light to the same output. The output of the EDC is then focused on the end of a liquid light guide. The opposite end of the light guide is equipped with a microscope-coupling adapter thus presenting excitation light to the specimen. Microscope couplings are available for all commercial microscopes.
Two more recent innovations that are not illustrated in the figure are the Cube Flipper and the Filter Flipper. The cube flipper permits the EDC to be rotated out of the optical path so that all excitation light can be brought to the microscope. This feature permits quick alternation between dual excitation (i.e. fura-2) and single excitation (i.e. GFP) modes. The Filter Flipper is a manually controlled, 6-position filter wheel that is used to hold neutral density filters.
Excitation filters of your specification are included with each system and can be ordered as required.
Resources
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: Murine Cardiomyocyte Isolation
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: IonWizard Experiment Design
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: Calcium & Contractility System Acquisition Quick Start
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: CytoSolver Batch Analysis
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: Analyzing Unmarked Events
- IonOptix Video Tutorials: IonWizard Data Analysis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in high-fat diet-induced obesity: role of suppression of forkhead transcription factor and atrophy gene transcription.
- Vessel System HyperSwitch Config
- Replacing Your Xe Bulb
- Myocyte Calcium & Contractility Recording System (HyperSwitch Configuration)
- HyperSwitch Hardware Manual
- G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 ablation in cardiac myocytes before or after myocardial infarction prevents heart failure.
- Techniques and Best Practices for Cardiomyocyte Isolation
- Glucocorticoid- and protein kinase A-dependent transcriptome regulation in airway smooth muscle.
- Novel role of calpain-3 in the triad-associated protein complex regulating calcium release in skeletal muscle.
- Type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors mediate UTP-induced cation currents, Ca2+ signals, and vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries.
- Role of the transcription factor sox4 in insulin secretion and impaired glucose tolerance.
- Reactive oxygen species mediate RhoA/Rho kinase-induced Ca2+ sensitization in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle following chronic hypoxia.
- Maturation of intracellular calcium homeostasis in sheep pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.
- Adenosine A2A and beta-adrenergic calcium transient and contractile responses in rat ventricular myocytes.
- Action potential characterization in intact mouse heart: steady-state cycle length dependence and electrical restitution.
- Actin cytoskeletal modulation of pressure-induced depolarization and Ca(2+) influx in cerebral arteries.
- Abnormal Motility in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines
Note: This product is intended for research purposes only. It is not certified for clinical applications (including diagnostic purposes). Use of this product in uncertified applications is in violation of FDA regulations.